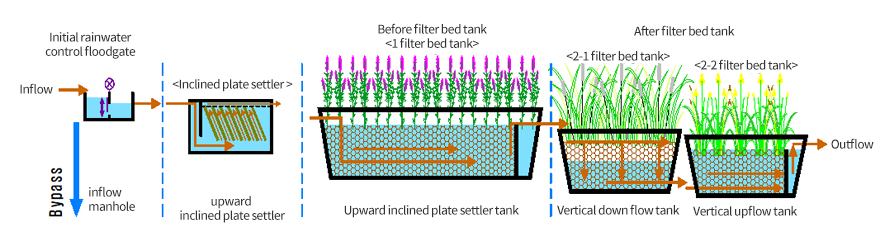
EADS constructed wetland test bed construction
Phosphorus Removal Mechanism of Constructed Wetlands
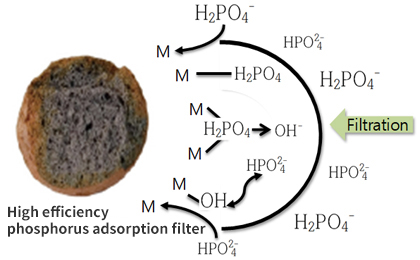
Adsorption and filtration by high-efficiency phosphorus adsorption media
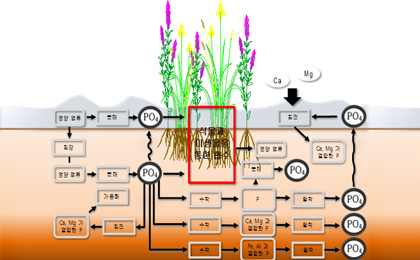
Sedimentation in soil, absorption of plants, removal by microorganisms
Process-specific processing mechanisms
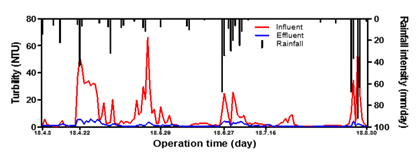
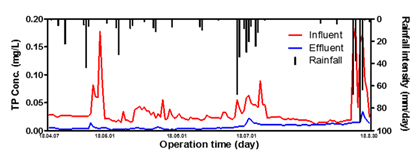
T-P mass balance for each EADS process
| Process |
Inflow load(㎏) |
Outflow load(㎏) |
Processing load(㎏) |
Removal rate(%) |
| EAD process |
170 |
51 |
118 |
70 |
| A sedimentary land |
170 |
85 |
84 |
50 |
| 1 Yeo Sang-jo |
85 |
69 |
16 |
10 |
| 2 Yeo Sang-jo |
68 |
51 |
18 |
10 |
T-P Mass balance by Yeo Sang-jo Mechanism/h5>
| Process |
Processing load(㎏) |
Filtration and precipitation(㎏) /
Contribution rate(%) |
Adsorption of media(㎏) /
Contribution rate(%) |
Absorption of plants(㎏) /
Contribution rate(%) |
| 1 Yeo Sang-jo |
16 |
0.680 / 4.2 |
9.513 / 58 |
6.215 / 38 |
| 2-1 Yeo Sang-jo |
16 |
0.030 / 0.2 |
9.460 / 60 |
6.199 / 40 |
| 2-2 Yeo Sang-jo |
2 |
0.002 / 0.1 |
0.036 / 2 |
1.890 / 98 |
- Most of the removal mechanism in settling paper is done by sedimentation, and the removal mechanism of filter paper consists of adsorption by filter media, filtration, sedimentation in soil, plant absorption, and removal by microorganisms.
- 1 Total phosphorus removed by filtration or sedimentation of the filter media was 4.2%, adsorption by filter media was 8%, and removal by plant absorption was 37.8%.
- 2-1 Yeosangjo shows 60.3% adsorption by filtrate and 39.5% absorption by plants, and 2-1 Yeosangjo shows 98% absorption by plants
- 2-2 Most of the total phosphorus introduced into the filtration area is absorbed by plants planted with dissolved phosphorus